中秋節 雖然過了~還是有feel一樣快樂~![]()
package com.tzu2.controllers;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import com.tzu2.domain.Member;
//有關於會員操作的控制器Controller
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path="/member")
public class MemberController {
//注入依賴物件DataSource
@Autowired
private DataSource datasource;
//註冊Action(Method)
@RequestMapping(path="/register",method= {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
public String register(@RequestParam(name="username")String userName
,String password,String email
,@RequestParam(name="realname")String realName) {
//如何判斷傳送方式採用GET(直接調用表單頁面) or POST(進行會員註冊作業 資料???)
System.out.println("register..."+userName);
//直接調用表單頁面(註冊表單)
return "memberregister";
}
//採用表單傳遞欄位進來之後 自動封裝到一個物件屬性去
//註冊Action(Method)
//參數按照型別 注入Injection該型別的物件
//透過方法注入Servlet api-HttpServletRequest
@RequestMapping(path="/registerform",method= {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
public String registerForm(Model model,Member member) {
//透過注入的依賴DataSource生產一個連接物件(連接上資料庫伺服器)
String message=null;
if(member.getUsername()!=null && member.getPassword()!=null) {
Connection connection=null;
try {
connection=datasource.getConnection();
System.out.println("資料庫:"+connection.getCatalog());
//借助Jdbc進行會員註冊作業
String sql="Insert Into webmember(username,password,email,realname,phone) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
//1.透過連接物件取出命令物件 配置新增SQL
PreparedStatement st=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//2.設定參數
st.setString(1,member.getUsername());
st.setString(2, member.getPassword());
st.setString(3, member.getEmail());
st.setString(4, member.getRealname());
st.setString(5, member.getPhone());
//3.完成新增作業
int affect=st.executeUpdate();
message="註冊成功!!!";
//4.設定訊息
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
//設定狀態訊息
message="會員名稱有問題!註冊失敗!!";
}finally {
//例外也好 正常也好 都要來這裡執行
if(connection!=null) {
//有開啟 進行關閉 將連接收集到Connection Pooling
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//要進行狀態持續 借助Model進行狀態持續 也就Thymeleaf template
model.addAttribute("message", message);
model.addAttribute("member", member);
//如何判斷傳送方式採用GET(直接調用表單頁面) or POST(進行會員註冊作業 資料???)
System.out.println("register..."+member.getUsername());
}
//直接調用表單頁面(註冊表單)
//帶整個member到畫面渲染
return "memberregister";
}
}
這是一個Spring MVC控制器的Java類,負責處理會員註冊相關的操作。讓我們來分解這段程式碼的關鍵部分:
@Controller:此註解表示這是一個Spring MVC控制器,用於處理HTTP請求。
@RequestMapping:這是類層級的@RequestMapping註解,設置了基本路徑,即/member。這表示該控制器處理的所有請求路徑都以/member開頭。
@Autowired:此註解用於將DataSource依賴項注入到控制器中。DataSource通常用於數據庫連接。
register 方法:這個方法處理/member/register路徑的GET和POST請求。它接受username、password、email 和 realName 作為參數,並返回"memberregister"視圖。然而,該方法目前僅輸出一條訊息,而不執行任何會員註冊操作。
registerForm 方法:這個方法處理/member/registerform路徑的GET和POST請求。它接受一個Model對象和一個Member對象作為參數。這個方法的主要功能包括:
Member對象的屬性。Model中,以供視圖顯示。最後,return "memberregister" 用於返回名為"memberregister"的視圖,並將註冊訊息和 Member 對象傳遞給視圖,以供顯示。
總之,這個控制器用於處理會員註冊操作。當用戶訪問/member/register或/member/registerform路徑時,該控制器處理相應的請求,接收用戶輸入的註冊信息,並在數據庫中執行註冊操作。然後,它返回一個視圖,並在視圖中顯示註冊結果訊息。
package com.tzu2.domain;
public class Member implements java.io.Serializable {
//Attribute
private String username;
private String password;
private String realname;
private String email;
private String phone;
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getRealname() {
return realname;
}
public void setRealname(String realname) {
this.realname = realname;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
前端程式碼:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>註冊作業</title>
</head>
<body>
<fieldset>
<legend>註冊作業</legend>
<!--設計表單-->
<form method="post">
<div>
<div>使用者帳號</div>
<input type="text" th:value="${member.username}" name="username"/>
</div>
<div>
<div>使用者密碼</div>
<input type="password" th:value="${member.password}" name="password"/>
</div>
<div>
<div>真實姓名</div>
<input type="text" th:value="${member.realname}" name="realname"/>
</div>
<div>
<div>EMAIL</div>
<input type="text" th:value="${member.email}" name="email"/>
</div>
<div>
<div>連絡電話</div>
<input type="text" th:value="${member.phone}" name="phone"/>
</div>
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="註冊"/>
</form>
<div><h3 th:text="${message}"></h3></div>
</fieldset>
</body>
</html>
這是一個HTML表單,用於註冊作業的網頁。以下是HTML代碼的主要組件:
<meta> 標籤:用於定義網頁的字符集和瀏覽器相容性。
<title> 標籤:設置網頁的標題,顯示在瀏覽器的標題欄中。
<fieldset> 和 <legend>:用於組織和標題化表單元素,提供結構性信息。
<form> 標籤:定義HTML表單,並使用 "post" 方法來提交表單數據。
<input> 元素:用於輸入數據。
type="text" 的 <input> 元素用於輸入文本數據,例如使用者帳號、真實姓名、EMAIL和連絡電話。type="password" 的 <input> 元素用於輸入密碼數據,例如使用者密碼。th:value="${member.xxx}":這些屬性用於使用Thymeleaf模板引擎,以將後端的member物件的屬性值填充到對應的 <input> 元素中,實現數據的預填充。
<br/>:用於插入斷行,創建間距。
<input type="submit">:提交表單的按鈕,用戶點擊後提交表單數據。
<h3> 標籤:顯示註冊後的訊息,使用Thymeleaf的 th:text 屬性將後端的 message 填充到 <h3> 標籤中。
這個HTML表單可用於註冊使用者,使用者可以填寫帳號、密碼、真實姓名、EMAIL和連絡電話,然後點擊"註冊"按鈕提交數據。網頁上方的 <title> 標籤設置了網頁的標題為"註冊作業"。
測試http://localhost:8080/member/registerform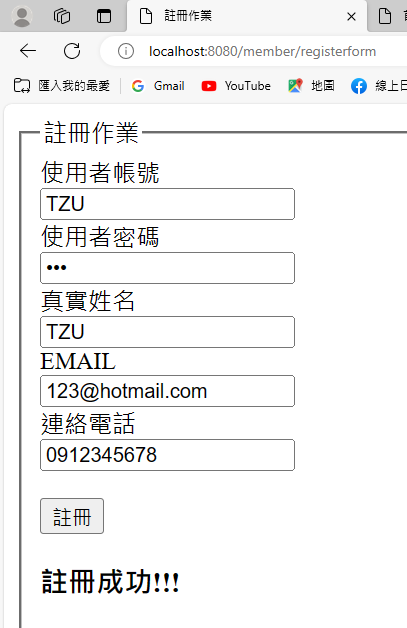
增加一個檔案:CustomersController
package com.tzu.controllers;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path="/customers")
public class CustomersController {
//Attribute(Data Field) Field Injection
//查詢功能設計
@RequestMapping(path="/qry/country",
method= {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
public String customersQry(String country) {
return "customersqrycountry";
}
}
這是一個 Spring MVC 控制器,處理有關顧客的查詢功能。以下是控制器中的一些關鍵點:
@Controller:這個註解標記類別為Spring MVC控制器,告訴Spring這個類別包含處理HTTP請求的方法。
@RequestMapping:這個註解用於指定控制器處理的請求路徑的前綴,也就是當URL以 "/customers" 開頭時,這個控制器會處理相關的請求。
customersQry 方法:這是一個處理查詢的方法,它處理 /customers/qry/country 路徑的 GET 和 POST 請求。當使用者發出這個請求時,該方法會接受一個名為 "country" 的參數。
String country:這個方法的參數 country 用於接收用戶在請求中提供的國家參數。方法返回值:這個方法返回一個字符串 "customersqrycountry"。通常,這表示控制器將渲染名為 "customersqrycountry" 的視圖(View)。這個視圖是一個HTML模板或JSP文件,用於呈現查詢國家的結果。
總之,這個控制器設計用於處理有關顧客查詢國家的請求,它接受國家作為參數,然後可能將結果顯示在相應的視圖上。需要確保有一個名為 "customersqrycountry" 的視圖模板,以便它可以正確呈現查詢的結果。
再增加一個html檔
當然也是要用VSCODE編輯~然後再同步到後端
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>客戶資料查詢</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--表單頁面-->
<form method="post">
<div>國家別</div>
<input type="text" name="country" th:value="${country}"/>
<input type="submit" value="查詢"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
測試看看http://localhost:8080/customers/qry/country
這是一個 HTML 表單頁面,用於接受客戶查詢的國家別。以下是這個表單頁面的關鍵點:
form 標籤:表單的起始標籤,使用 method="post" 來指定當用戶提交表單時將使用 POST 請求。
input 標籤:用於接受用戶輸入的國家別。這個 input 元素的 name 屬性為 "country",這對應到控制器方法 customersQry 中的參數名稱。
th:value="${country}":這個屬性表示使用Thymeleaf模板引擎來填充 input 元素的值。${country} 是Thymeleaf的變數,它將由控制器方法設定,然後填充到這個 input 元素中。
input 標籤(第二個):這是一個提交按鈕,用戶可以點擊它來提交表單。
這個表單頁面用於接受用戶輸入的國家別,然後當用戶點擊 "查詢" 按鈕時,表單的內容將以 POST 請求的形式傳遞給相應的控制器方法。該控制器方法將處理查詢操作,並可能返回相關的結果。
希望成功~
先講解資料庫裏面是有view資料表
SQL VIEW 檢視表 / 視圖 - SQL 語法教學 Tutorial
View 是藉由 SQL SELECT 查詢動態組合生成的資料表 (亦即 View 是由查詢得到的結果集組合而成的資料表)。View 內的資料紀錄是由其它實際存在的資料表中產生的,它就像是一個虛擬資料表,實際上資料庫 (或說是硬碟)…
www.fooish.com
先試著創建~
先有一個table
CREATE TABLE `customer` (
`ID` varchar(30) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(30) NOT NULL,
`address` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`zipcode` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`phone` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`city` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`country` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`notes` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`SID` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci COMMENT='國家資料表';
創建等等要用的view資料表
CREATE VIEW customer_list
AS SELECT ID,name,address,zipcode,phone,city,country,notes,SID
FROM customer;
先在裡面填入資料
也試著view查詢
Select * From customer_list Where country='Taiwan'
再改一下前端程式碼增加POST
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>客戶資料查詢</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--表單頁面-->
<form method="post">
<div>國家別</div>
<input type="text" name="country" th:value="${country}"/>
<input type="submit" value="查詢"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
這是一個 HTML 表單頁面,用於接受客戶的國家別查詢。以下是這個表單頁面的要點:
form 標籤:這是表單的起始標籤,它指定了使用 POST 方法提交表單。
input 標籤:這個 input 元素用於接受用戶輸入的國家別。name 屬性為 "country",這個名稱將在後端控制器中用於識別該輸入字段。
th:value="${country}":這是Thymeleaf模板引擎的語法,用於填充 input 元素的值。${country} 是一個Thymeleaf變數,它將由後端控制器設置,並將其值填充到這個 input 元素中。
第二個 input 標籤:這是提交按鈕,用戶可以點擊它來提交表單。
總之,這個表單允許用戶輸入國家別,當他們點擊 "查詢" 按鈕時,表單將被提交到後端控制器進行處理,以執行相關的查詢操作。表單中的 th:value 屬性確保在頁面首次載入時,如果有任何舊的查詢值,它們將被填充到輸入框中,以供用戶參考或修改。
後端程式碼:
package com.tzu.controllers;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path="/customers")
public class CustomersController {
//Attribute(Data Field) Field Injection
//查詢功能設計
@RequestMapping(path="/qry/country",
method= {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
public String customersQry(String country) {
//是否第一次請求 沒有傳遞國家別
if(country==null) {
return "customersqrycountry"; //View Page名稱
}else {
System.out.println("查詢國家別:"+country);
return "customersqrycountry";
}
}
}
CustomersController 中的 customersQry 方法負責處理客戶查詢國家別的功能。以下是方法的關鍵點:
@RequestMapping 注解:這個注解指定了處理這個方法的請求路徑,即 /customers/qry/country,並且指定了可以處理 GET 和 POST 請求。
方法參數:這個方法接受一個參數 String country,這是從前端表單傳遞過來的國家別。如果在請求中未傳遞國家別,則該參數將為 null。
方法邏輯:在方法內部,首先檢查 country 參數是否為 null,如果是,則表示這是第一次請求,並且用戶尚未提交國家別查詢。在這種情況下,它將返回 "customersqrycountry",這個名稱通常對應於Thymeleaf模板視圖。
如果 country 參數不是 null,則表示用戶已提交國家別查詢,該方法將在控制台中印出查詢的國家別,然後仍然返回 "customersqrycountry"。
總之,這個方法處理客戶查詢國家別的操作。如果國家別未提交,它將顯示查詢表單視圖,如果提交了國家別,則它會處理查詢,然後仍然顯示查詢表單視圖。
再測試看看:http://localhost:8080/customers/qry/country
後端回傳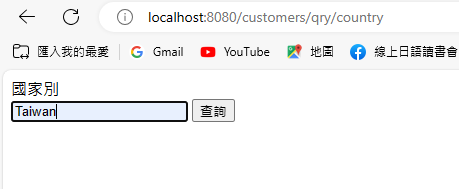
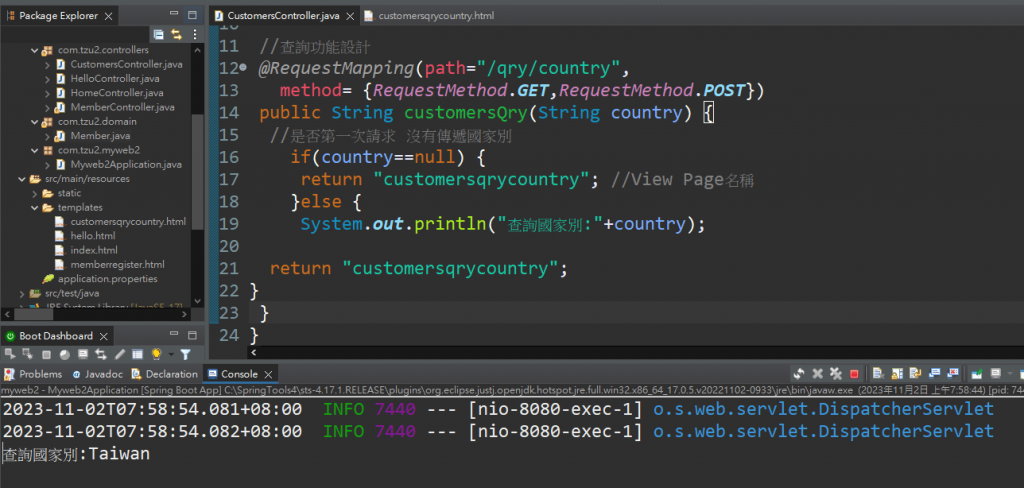
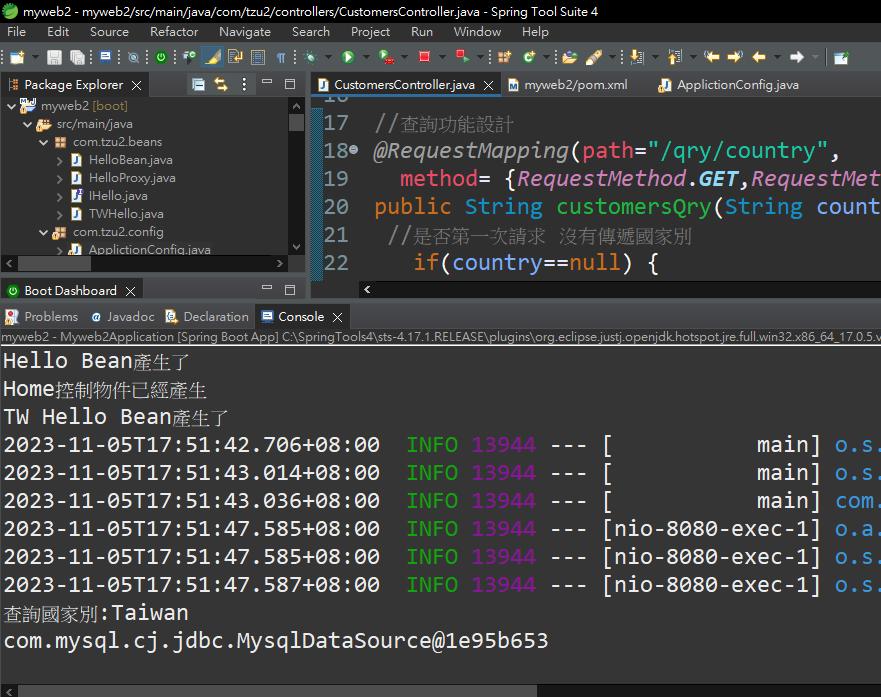
接下來要裝:https://mvnrepository.com/search?q=spring+boot+jdbc
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
目前配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.12</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.tzu2</groupId>
<artifactId>myweb2</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>myweb2</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.31</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Spring Boot Starter Data JDBC
貼到系統設定
修改ApplictionConfig並測試看看有沒有注入
@Bean //生命週期每一個注入 產生一個體
public JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource datasource) {
//建構JdbcTemplate物件
System.out.println(“JdbcTemplate 注入的DataSource:”+datasource.toString());
JdbcTemplate template=new JdbcTemplate();
template.setDataSource(datasource); //Property Injection屬性注入依賴物件
return template;
}
package com.tzu.config;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlDataSource;
import com.tzu.beans.HelloBean;
import com.tzu.beans.HelloProxy;
import com.tzu.beans.IHello;
import com.tzu.beans.TWHello;
//透過方法生產Bean物件 註冊到Spring容器去
@Configuration
public class ApplictionConfig {
//Attribute 使用spEL ${}
//@Value標註取出預設組態application.properties設定項目
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String userName;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
public ApplictionConfig() {
System.out.println("Configuration Bean配置了");
}
//生產一個HelloBean物件
@Bean(name="hellonean")
public HelloBean getHelloBean() {
System.out.println("Hello Bean產生了");
//建構HelloBean
HelloBean hello=new HelloBean();
return hello;
}
@Bean
public TWHello getTWHello() {
System.out.println("TW Hello Bean產生了");
//建構HelloBean
TWHello hello=new TWHello();
return hello;
}
//參數使用定義Bean alias Name 注入依賴 隨著窗口物件注入到對方去 進行反轉物件注入
@Bean
public HelloProxy getHelloProxy(TWHello bean) {
var helloProxy=new HelloProxy(bean);
return helloProxy;
}
//產生一個DataSource 是共用的物件(連接物件工廠 整個應用系統工廠只要一個即可)
@Bean
public DataSource createDataSource() {
System.out.println("Datasource:"+this.url);
//建構MySQLDataSource
MysqlDataSource datasource=new MysqlDataSource();
//配置要件 URL/User name/password
datasource.setUrl(url);
datasource.setUser(userName);
datasource.setPassword(password);
//Driver 會進行內部使用
return datasource;
}
//生產JdbcTemplate元件(Spring Bean)
//透過IoC注入控制反轉 注入DataSource物件
@Bean //生命週期每一個注入 產生一個體
public JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource datasource) {
//建構JdbcTemplate物件
System.out.println("JdbcTemplate 注入的DataSource:"+datasource.toString());
JdbcTemplate template=new JdbcTemplate();
template.setDataSource(datasource); //Property Injection屬性注入依賴物件
return template;
}
}
這段程式碼是一個Java Spring的配置檔案,主要用於設定和定義Spring應用程式中的bean和它們的相依性。以下是這段程式碼的主要內容:
@Configuration:這個註解表示這個類別是Spring應用程式上下文的配置類別。它定義和配置Spring bean。
@Value:這些註解用於將外部屬性檔案(通常是application.properties)中的值注入到相應的字段中。例如,@Value("${spring.datasource.url}") 將spring.datasource.url 的值注入到 url 字段中。
@Bean:這些註解定義了方法,用來建立和配置Spring bean。這些方法由Spring容器調用,並返回的物件在應用程式上下文中被管理為bean。
public ApplictionConfig():這是配置類別的建構函式。它在載入配置類別時執行,提供了一個印出當它被呼叫時的訊息。
getHelloBean():這個方法定義一個名為 "hellonean" 的bean,並返回一個 HelloBean 物件。
getTWHello():這個方法定義一個型別為 TWHello 的bean。
getHelloProxy(TWHello bean):這個方法定義了一個名為 "helloProxy" 的bean,它依賴於一個 TWHello bean。它建立一個 HelloProxy 物件,使用提供的 TWHello bean。
createDataSource():這個方法定義了一個用於DataSource(可能是MySQL資料庫)的bean。它根據從屬性檔案中擷取的URL、使用者名稱和密碼的值來配置資料來源。
createJdbcTemplate(DataSource datasource):這個方法定義了一個JdbcTemplate的bean,這是用於資料庫訪問的Spring元件。它將之前定義的DataSource bean注入到JdbcTemplate中,並將其設置為一個屬性。
總結,這個配置檔案定義了幾個Spring bean,包括 HelloBean、TWHello 和 JdbcTemplate,並管理它們的相依性,如將資料來源注入到JdbcTemplate中。它還從外部的配置檔案讀取屬性,並使用這些值來配置bean,如資料來源的URL和認證資訊。
再加入@Scope(“singleton”)
package com.tzu.config;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlDataSource;
import com.tzu.beans.HelloBean;
import com.tzu.beans.HelloProxy;
import com.tzu.beans.IHello;
import com.tzu.beans.TWHello;
//透過方法生產Bean物件 註冊到Spring容器去
@Configuration
public class ApplictionConfig {
//Attribute 使用spEL ${}
//@Value標註取出預設組態application.properties設定項目
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String userName;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String password;
public ApplictionConfig() {
System.out.println("Configuration Bean配置了");
}
//生產一個HelloBean物件
@Bean(name="hellonean")
public HelloBean getHelloBean() {
System.out.println("Hello Bean產生了");
//建構HelloBean
HelloBean hello=new HelloBean();
return hello;
}
@Bean
public TWHello getTWHello() {
System.out.println("TW Hello Bean產生了");
//建構HelloBean
TWHello hello=new TWHello();
return hello;
}
//參數使用定義Bean alias Name 注入依賴 隨著窗口物件注入到對方去 進行反轉物件注入
@Bean
public HelloProxy getHelloProxy(TWHello bean) {
var helloProxy=new HelloProxy(bean);
return helloProxy;
}
//產生一個DataSource 是共用的物件(連接物件工廠 整個應用系統工廠只要一個即可)
@Bean
@Scope("singleton")
public DataSource createDataSource() {
System.out.println("Datasource:"+this.url);
//建構MySQLDataSource
MysqlDataSource datasource=new MysqlDataSource();
//配置要件 URL/User name/password
datasource.setUrl(url);
datasource.setUser(userName);
datasource.setPassword(password);
//Driver 會進行內部使用
return datasource;
}
//生產JdbcTemplate元件(Spring Bean)
//透過IoC注入控制反轉 注入DataSource物件
@Bean //生命週期每一個注入 產生一個體
public JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource datasource) {
//建構JdbcTemplate物件
System.out.println("JdbcTemplate 注入的DataSource:"+datasource.toString());
JdbcTemplate template=new JdbcTemplate();
template.setDataSource(datasource); //Property Injection屬性注入依賴物件
return template;
}
}
這段程式碼仍然是一個Java Spring的配置檔案,但有一個小改變:在createDataSource()方法上使用了@Scope("singleton")註解,這表示DataSource bean 的作用範圍是單例(singleton)。這個設定將使Spring容器在應用程式生命週期中只建立一個DataSource bean,並在需要時重複使用它。
其他部分的功能和說明仍然相同,以下是對這段程式碼的主要內容的簡要說明:
@Scope("singleton"):這個註解用於設定bean的作用範圍。在這個例子中,DataSource bean 的作用範圍被設定為singleton,這意味著只會有一個DataSource bean 實例存在於Spring容器中。
createDataSource() 方法:這個方法仍然用於定義一個DataSource bean,但現在它是一個單例bean。這個bean用於建立資料庫連線,並配置URL、使用者名稱和密碼。
createJdbcTemplate(DataSource datasource) 方法:這個方法定義了一個JdbcTemplate的bean,它仍然注入了之前定義的DataSource bean,但現在DataSource bean是單例。這個bean用於執行資料庫查詢。
總結,這個配置檔案主要是用來定義和配置Spring bean,並且在此版本中,DataSource bean 被設定為單例,以提高效能,並確保在應用程式中只有一個DataSource 實例。其他部分的功能和目的與之前的版本相同。
這時資料庫view先用sql語法測試
Select * From customer_list Where country='Taiwan'
再修改CustomersController插入@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //DataSource會注入控制反轉
package com.tzu.controllers;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path="/customers")
public class CustomersController {
//Attribute(Data Field) Field Injection
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //DataSource會注入控制反轉
//查詢功能設計
@RequestMapping(path="/qry/country",
method= {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
public String customersQry(String country) {
//是否第一次請求 沒有傳遞國家別
if(country==null) {
return "customersqrycountry"; //View Page名稱
}else {
System.out.println("查詢國家別:"+country);
DataSource ds=jdbcTemplate.getDataSource();
System.out.println(ds.toString());
return "customersqrycountry";
}
}
}
這段程式碼是一個Spring控制器(Controller),它處理Web應用程式的HTTP請求和回應。以下是對這段程式碼的主要內容的簡要說明:
@Controller:這個註解表示這個類別是一個Spring MVC控制器,它會處理HTTP請求。
@RequestMapping:這個註解用於定義控制器處理的HTTP請求路徑。在這個例子中,所有與"/customers"路徑相關的請求都將由這個控制器處理。
@Autowired:這個註解用於依賴注入,它將jdbcTemplate 注入到這個控制器中。jdbcTemplate 是一個JdbcTemplate bean,它是用於執行資料庫查詢的Spring組件。
customersQry 方法:這個方法處理對"/customers/qry/country"路徑的HTTP GET和POST請求。它接受一個名為country 的參數,用於查詢客戶資料。
如果 country 參數是null,表示這是第一次請求,它將返回一個View Page的名稱 "customersqrycountry",這個View Page將用於輸入國家別的查詢。
如果 country 參數不是null,表示已經傳遞了國家別,它會顯示查詢的國家別,並且透過 jdbcTemplate 取得資料庫連線物件 DataSource,然後將它印出來。
這個控制器主要用於處理客戶資料的查詢,並且它依賴於jdbcTemplate,這個jdbcTemplate 是透過控制反轉(IoC)由Spring容器注入的。
總結,這個控制器處理與"/customers/qry/country"路徑相關的HTTP請求,並使用Spring的依賴注入功能,將jdbcTemplate 注入到控制器中,以便在方法中執行資料庫查詢。
再用客戶資料查詢http://localhost:8080/customers/qry/country 測試
產生的樣子:
再增加一個檔案Customer.java
package com.tzu.domain;
//JavaBean 封裝每一筆客戶資料
public class Customer implements java.io.Serializable {
//Attribute
private short id;
private String name;
private String address;
private String phone;
private String country;
public short getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(short id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
}
這段程式碼定義了一個JavaBean,稱為 Customer,用於封裝客戶資料。以下是 Customer 類別的主要特點:
Customer 類別實作了 java.io.Serializable 介面,這表示它可以被序列化,通常用於將物件轉換成位元組以便於儲存或傳輸。
Customer 類別具有一些私有(private)屬性,這些屬性用於存儲客戶資料,包括:
id(短整數):客戶的唯一識別符。name(字串):客戶的名稱。address(字串):客戶的地址。phone(字串):客戶的電話號碼。country(字串):客戶的國家。對於每個屬性,都有一個公開的getter(取值方法)和setter(設值方法)方法,用於訪問和設置相應的屬性值。這遵循了JavaBean的標準約定,讓外部程式可以存取和修改這些屬性。
這個 Customer 類別用於封裝客戶資料,允許您創建 Customer 物件,並設置或檢索相關的客戶資訊。這樣的JavaBean常常在應用程式中用於儲存和處理資料。
再更改CustomersController
package com.tzu.controllers;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.tzu.domain.Customer;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path="/customers")
public class CustomersController {
//Attribute(Data Field) Field Injection
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //DataSource會注入控制反轉
//查詢功能設計
@RequestMapping(path="/qry/country",
method= {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
public String customersQry(String country) {
//是否第一次請求 沒有傳遞國家別
if(country==null) {
return "customersqrycountry"; //View Page名稱
}else {
System.out.println("查詢國家別:"+country);
DataSource ds=jdbcTemplate.getDataSource();
System.out.println(ds.toString());
//1.採用DAO設計模式(Spring Boot data jdbc)
String sql="SELECT ID,name,address,phone,country "
+ "FROM sakila.customer_list where country=?";
//2.進行國家別相關客戶查詢
List<Customer> result=jdbcTemplate.query(sql,
//傳遞一個程序當作參數(RowMapper/maprow 介面) 使用Lambda
//查詢符合每一筆 逐筆傳遞進來callback 自訂程序封裝結果
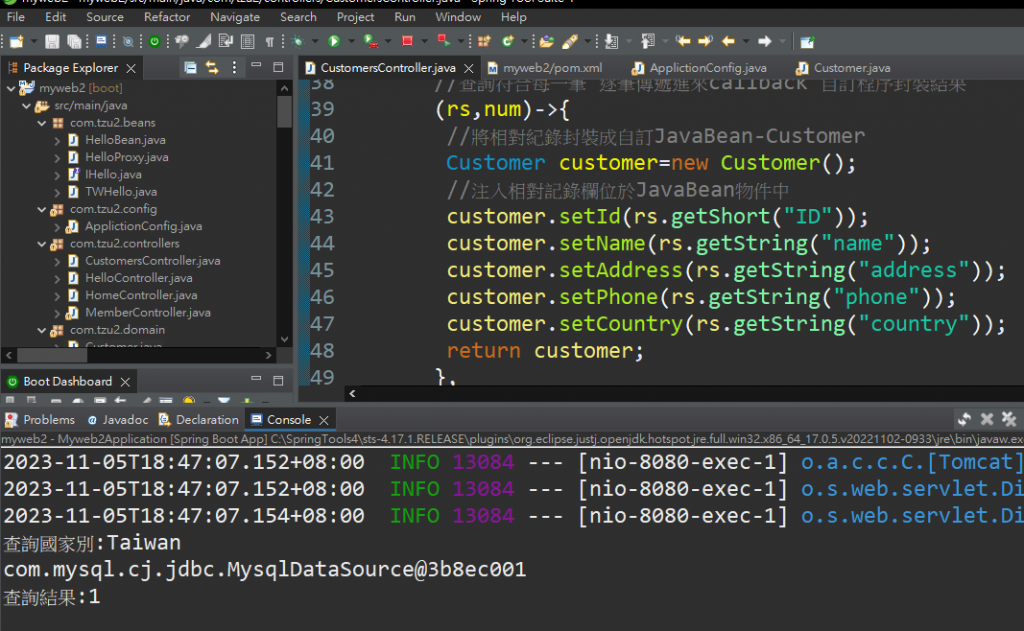
(rs,num)->{
//將相對紀錄封裝成自訂JavaBean-Customer
Customer customer=new Customer();
//注入相對記錄欄位於JavaBean物件中
customer.setId(rs.getShort("ID"));
customer.setName(rs.getString("name"));
customer.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
customer.setPhone(rs.getString("phone"));
customer.setCountry(rs.getString("country"));
return customer;
},
country
);
System.out.println("查詢結果:"+result.size());
return "customersqrycountry";
}
}
}
這段程式碼是一個Spring控制器(Controller),用於處理客戶資料的查詢功能。以下是對這段程式碼的主要內容的簡要說明:
@Controller:這個註解表示這個類別是一個Spring MVC控制器,它會處理HTTP請求。
@RequestMapping:這個註解用於定義控制器處理的HTTP請求路徑。在這個例子中,所有與"/customers"路徑相關的請求都將由這個控制器處理。
@Autowired:這個註解用於依賴注入,它將jdbcTemplate 注入到這個控制器中。jdbcTemplate 是一個JdbcTemplate bean,它用於執行資料庫查詢。
customersQry 方法:這個方法處理對"/customers/qry/country"路徑的HTTP GET和POST請求。它接受一個名為country 的參數,用於查詢客戶資料。
如果 country 參數是null,表示這是第一次請求,它將返回一個View Page的名稱 "customersqrycountry",這個View Page將用於輸入國家別的查詢。
如果 country 參數不是null,表示已經傳遞了國家別,它會顯示查詢的國家別,然後執行資料庫查詢操作:
定義SQL查詢語句,並將country 參數作為查詢的條件。
使用 jdbcTemplate.query() 方法執行查詢,並將查詢結果封裝成 Customer 物件的清單。這是透過傳遞一個Lambda表示式給 jdbcTemplate.query(),用於將查詢結果的每一筆記錄對映到一個 Customer 物件中。
最後,將查詢結果的大小印出。
這個控制器的主要功能是根據輸入的國家別查詢客戶資料,並且使用Spring的依賴注入功能,將jdbcTemplate 注入到控制器中,以便執行資料庫查詢。查詢結果是通過將每一條記錄對映到 Customer 物件中,然後放入結果列表中。
測試查出幾筆是Taiwan資料http://localhost:8080/customers/qry/country
謝謝收看![]()
